Vue 3 自定义 Hooks 完全指南
一、Hooks 基础概念
1. 什么是 Hooks
Hooks 是 Vue 3 Composition API 中一个重要的概念,它允许我们:
- 提取和复用组件逻辑
- 保持状态的响应性
- 实现关注点分离
2. Hooks 的特点
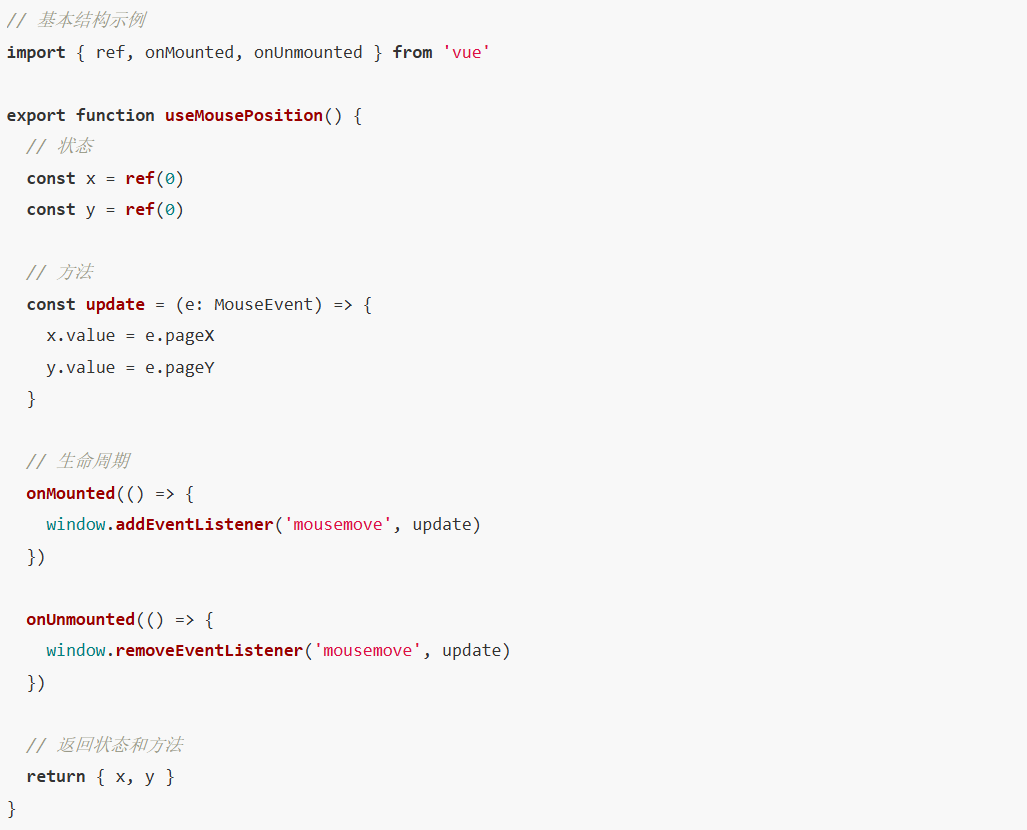
二、常用 Hooks 实现
1. 网络请求 Hook
// hooks/useRequest.ts
import { ref, shallowRef } from 'vue'
import type { AxiosRequestConfig, AxiosResponse } from 'axios'
export interface RequestOptions extends AxiosRequestConfig {
immediate?: boolean
onSuccess?: (data: any) => void
onError?: (error: any) => void
}
export function useRequest<T = any>(
url: string,
options: RequestOptions = {}
) {
const data = shallowRef<T | null>(null)
const error = shallowRef<any>(null)
const loading = ref(false)
const {
immediate = true,
onSuccess,
onError,
...axiosConfig
} = options
const execute = async () => {
loading.value = true
error.value = null
try {
const response = await axios.request<T>({
url,
...axiosConfig
})
data.value = response.data
onSuccess?.(response.data)
return response
} catch (err) {
error.value = err
onError?.(err)
throw err
} finally {
loading.value = false
}
}
if (immediate) {
execute()
}
return {
data,
error,
loading,
execute
}
}
// 使用示例
const {
data: users,
loading,
error,
execute: fetchUsers
} = useRequest<User[]>('/api/users', {
immediate: false,
onSuccess: (data) => {
console.log('Users loaded:', data)
}
})
2. 状态管理 Hook
// hooks/useState.ts
import { reactive, readonly } from 'vue'
export function useState<T extends object>(
initialState: T,
options: {
persist?: boolean
key?: string
} = {}
) {
const { persist = false, key = 'app_state' } = options
// 初始化状态
const state = reactive({
...initialState,
...(persist ? JSON.parse(localStorage.getItem(key) || '{}') : {})
})
// 修改状态方法
const setState = (partial: Partial<T> | ((state: T) => Partial<T>)) => {
const newState = typeof partial === 'function' ? partial(state) : partial
Object.assign(state, newState)
if (persist) {
localStorage.setItem(key, JSON.stringify(state))
}
}
// 重置状态
const resetState = () => {
Object.assign(state, initialState)
if (persist) {
localStorage.removeItem(key)
}
}
return {
state: readonly(state),
setState,
resetState
}
}
// 使用示例
const {
state: userState,
setState: setUserState,
resetState: resetUserState
} = useState({
name: '',
age: 0,
preferences: {}
}, {
persist: true,
key: 'user_state'
})
3. DOM 操作 Hook
// hooks/useElementSize.ts
import { ref, onMounted, onUnmounted } from 'vue'
export function useElementSize() {
const element = ref<HTMLElement | null>(null)
const width = ref(0)
const height = ref(0)
const observer = new ResizeObserver(entries => {
for (const entry of entries) {
const { contentRect } = entry
width.value = contentRect.width
height.value = contentRect.height
}
})
onMounted(() => {
if (element.value) {
observer.observe(element.value)
}
})
onUnmounted(() => {
observer.disconnect()
})
return {
element,
width,
height
}
}
// 使用示例
const { element, width, height } = useElementSize()
</script>
<template>
<div ref="element">
Size: {{ width }} x {{ height }}
</div>
</template>
4. 表单处理 Hook
// hooks/useForm.ts
import { reactive, computed } from 'vue'
interface FormOptions<T> {
initialValues: T
validate?: (values: T) => Promise<void>
onSubmit?: (values: T) => Promise<void>
}
export function useForm<T extends object>({
initialValues,
validate,
onSubmit
}: FormOptions<T>) {
const values = reactive({ ...initialValues })
const errors = reactive<Record<string, string>>({})
const touched = reactive<Record<string, boolean>>({})
const dirty = computed(() =>
Object.keys(initialValues).some(key =>
values[key as keyof T] !== initialValues[key as keyof T]
)
)
const handleSubmit = async () => {
try {
if (validate) {
await validate(values)
}
if (onSubmit) {
await onSubmit(values)
}
} catch (error) {
if (error instanceof Error) {
errors['form'] = error.message
}
}
}
const handleReset = () => {
Object.assign(values, initialValues)
Object.keys(errors).forEach(key => delete errors[key])
Object.keys(touched).forEach(key => delete touched[key])
}
const setFieldValue = (field: keyof T, value: any) => {
values[field] = value
}
const setFieldTouched = (field: keyof T, isTouched = true) => {
touched[field] = isTouched
}
return {
values,
errors,
touched,
dirty,
handleSubmit,
handleReset,
setFieldValue,
setFieldTouched
}
}
// 使用示例
const {
values,
errors,
touched,
handleSubmit
} = useForm({
initialValues: {
username: '',
password: ''
},
validate: async (values) => {
if (!values.username) {
throw new Error('Username is required')
}
},
onSubmit: async (values) => {
await api.login(values)
}
三、高级 Hooks 模式
1. 组合 Hooks
// hooks/useUserProfile.ts
export function useUserProfile(userId: string) {
// 组合多个基础 Hooks
const { data: user, loading: userLoading } = useRequest(
`/api/users/${userId}`
)
const { data: posts, loading: postsLoading } = useRequest(
`/api/users/${userId}/posts`
)
const loading = computed(() => userLoading.value || postsLoading.value)
return {
user,
posts,
loading
}
}
2. 条件 Hooks
// hooks/useConditional.ts
export function useConditionalFetch<T>(
url: string,
condition: () => boolean
) {
const { data, execute } = useRequest<T>(url, { immediate: false })
watch(
condition,
(value) => {
if (value) {
execute()
}
},
{ immediate: true }
)
return { data }
}
3. 缓存 Hooks
// hooks/useCache.ts
export function useCache<T>(
key: string,
factory: () => Promise<T>,
options: {
ttl?: number
} = {}
) {
const cache = new Map<string, {
data: T
timestamp: number
}>()
const getData = async () => {
const cached = cache.get(key)
if (cached && Date.now() - cached.timestamp < (options.ttl || 5000)) {
return cached.data
}
const data = await factory()
cache.set(key, {
data,
timestamp: Date.now()
})
return data
}
return { getData }
}
四、性能优化
1. 避免重复创建
// 使用 Symbol 确保唯一性
const stateSymbol = Symbol('state')
export function useState() {
const vm = getCurrentInstance()
if (!vm) {
throw new Error('useState must be called inside setup')
}
// 检查是否已存在
if (vm[stateSymbol]) {
return vm[stateSymbol]
}
// 创建新实例
const state = reactive({})
vm[stateSymbol] = state
return state
}
2. 合理使用 shallowRef
// 对于大型对象使用 shallowRef
export function useLargeData() {
const data = shallowRef<BigData | null>(null)
const setData = (newData: BigData) => {
data.value = newData
}
return {
data,
setData
}
}
五、最佳实践
1.命名规范
- 使用 use 前缀
- 驼峰命名
- 语义化
2.返回值规范
- 返回对象而不是数组
- 提供完整的类型定义
- 保持一致的命名
3.错误处理
- 提供错误状态
- 合理的异常捕获
- 友好的错误信息
4.生命周期处理
- 及时清理副作用
- 避免内存泄漏
- 处理组件卸载
总结
本指南涵盖了:
- Hooks 的基本概念和使用
- 常用 Hooks 的实现
- 高级 Hooks 模式
- 性能优化策略
- 最佳实践建议
关键点:
- 逻辑复用
- 状态管理
- 性能优化
- 代码组织








